Explain what types of information can be obtained from a line spectrum
What will be an ideal response?
The element which created it, the line-of-sight velocity of the source, its rotation speed, temperature, the pressure of the gas emitting the radiation, and even its magnetic field may also be found.
You might also like to view...
A hotter star is brighter than a cooler star of the same size. Assume both are typical stars
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
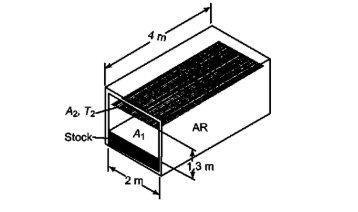
An electric furnace is to be used for batch heating a certain material with specific heat of 670 J/(kg K) from 20 to 760°C. The material is placed on the furnace floor which is 2m x 4m in area as shown in the accompanying sketch. The side walls of the furnace are made of a refractory material. Parallel to the plane of the roof, but several inches below it, a grid of round resistor rods is installed. The resistors are 13 mm in diameter and are spaced 5 cm center to center. The resistor temperature is to be maintained at 1100°C, under these conditions the emissivity of the resistor surface is 0.6. If the top surface of the stock is assumed to have an emissivity of 0.9, estimate the time required for heating a 6 metric ton batch. External heat losses from the furnace may be neglected, the
temperature gradient through the stock can be considered negligibly small, and steady-state conditions can be assumed.
GIVEN
- Batch heating of material in the furnace shown above
- Specific heat of material (c) = 670 Jkg K
- Material temperatures
- Initial 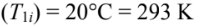
- Final 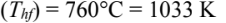
- Furnace dimensions: 2 m x 4 m x 1.3 m high
- Side walls are refractory material
- Resistor rod diameter (Dr) = 13 mm = 0.013 m
- Resistor center to center distance (s) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
- Resistor temperature (T2) = 1100°C = 1373 K
- Emissivity of the resistor surface (?2) = 0.6
- Emissivity of the material surface (?1) = 0.9
- Mass of material (m) = 6 metric tons = 6000 kg
FIND
- The time required (t) for heating the 6 metric ton batch
ASSUMPTIONS
- Quasi-steady state conditions
- External heat losses are negligible
- Temperature gradient through the material is negligible (negligible internal thermal resistance)
- Material is gray
- Convective heat transfer is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 x 10–8 W/(m2 K4
Steel blocks A and B, which have equal masses, are at TA = 300 °C and TB = 400 °C. Block C, with mC = 2mA, is at TC = 350 °C. Blocks A and B are placed in contact, isolated, and allowed to come into equilibrium. Then they are placed in contact with block C. At that instant,
a. TA = TB < TC. b. TA = TB = TC. c. TA = TB > TC. d. TA + TB = TC. e. TA ? TB = TC.
Intensity of Sound: A certain siren radiates sound uniformly in all directions. At a distance of 17 m from the siren, the intensity level is 49 db. How many watts of power does this siren put out? The threshold of human hearing is 1.0 × 10-12 W/m2.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).