Economists use the notation Q = f(L,K) to describe:
a) the financial relationship between the inputs that a firm uses and the outputs that it produces.
b) the level of output (Q) required to fully employ labour (L) and capital (K).
c) the flow of labour (L) and capital (K) services that are available when output is (Q).
d) the arithmetic relationship between the outputs that a firm uses and the inputs that it produces.
e) the technological relationship between the inputs that a firm uses and the outputs that it produces.
Ans: a) the financial relationship between the inputs that a firm uses and the outputs that it produces.
You might also like to view...
Buyers who buy in bulk are often offered discounts. This is an example of:
A) predatory pricing. B) first-degree price discrimination. C) third-degree price discrimination. D) second-degree price discrimination.
Which of the following statements best describes “bracket creep” within the U.S. income tax code?
a. Until the late 1970s, if real wages increased along with inflation, people were moved into higher tax brackets and owed a higher proportion of their income in taxes, even though their nominal income had not risen. b. After the late 1970s, if real wages increased along with inflation, people were moved into higher tax brackets and owed a higher proportion of their income in taxes, even though their nominal income had not risen. c. Until the late 1970s, if nominal wages increased along with inflation, people were moved into higher tax brackets and owed a higher proportion of their income in taxes, even though their real income had not risen. d. After the late 1970s, if nominal wages increased along with inflation, people were moved into higher tax brackets and owed a higher proportion of their income in taxes, even though their real income had not risen.
The current private sector unionization rate in the United States is closest to
A. 25.7 percent. B. 12.4 percent. C. 6.4 percent. D. 19.3 percent.
Refer to the figure below where the nominal interest rate equals 6% and the money supply equals 600. If the Federal Reserve wants to set the nominal interest rate at 10%, it must conduct open market ________ to set the money supply at ________. 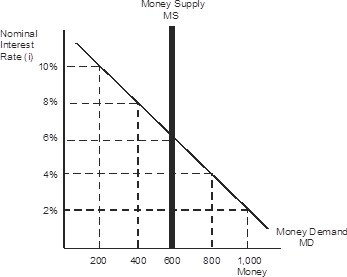
A. sales; 200 B. sales; 800 C. purchases; 800 D. purchases; 200