A disk (radius = 8.0 cm) that rotates about a fixed axis starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate to an angular velocity of 4.0 rad/s in 2.0 s. What is the magnitude of the total linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the disk at the instant when the angular velocity of the disk is 1.5 rad/s?
a. 24 cm/s2
b. 16 cm/s2
c. 18 cm/s2
d. 34 cm/s2
e. 44 cm/s2
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following best explains the hypothesized phenomenon of black hole evaporation?
A) Particles (or anti-particles) are created by a quantum mechanical effect near, but outside, the event horizon of the black hole. The law of conservation of energy maintains that the black hole must lose energy to "pay" for the creation of this mass. B) Particles (or anti-particles) are occasionally ejected from within the event horizon, causing the black hole to lose mass. C) Virtual particles created near the black hole are constantly annihilating each other, causing a high temperature even if the black hole has no accretion disk. This high temperature provides escape velocity for the virtual particles, causing the entire "cloud" of virtual particles to expand away into space. D) Black hole evaporation is a virtual process, meaning that it has been theorized by astrophysicists, but doesn't really occur.
Scattered light in the atmosphere is often partially polarized. The best way to determine whether or not light from a particular direction in the sky shows polarization is to
A. diffract the light through a single slit. B. squint while looking in that direction. C. rotate a piece of polaroid film about an axis parallel to the ray while looking through it in that sky direction. D. rotate a piece of polaroid film about an axis perpendicular to the ray while looking through it in that sky direction. E. reflect the rays from that direction on a shiny metal surface.
The figure below shows a planet traveling in a clockwise direction on an elliptical path around a star located at one focus of the ellipse. When the planet is at point A,
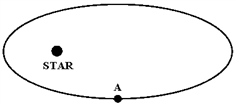
a.
its speed is constant.
b.
its speed is increasing.
c.
its speed is decreasing.
d.
its speed is a maximum.
e.
its speed is a minimum.
Develop a reasonable layout of nodes and control volumes for the geometry shown in the sketch. Provide a scale drawing showing the problem geometry overlaid with the nodes and control volumes.
GIVEN Two-dimensional transient conduction at an inside corner with specified-flux boundary condition FIND (a) The control volume energy balance equation,