A circular loop (area = 0.20 m2) turns in a uniform magnetic field with B = 0.13 T. At an instant when the angle between the magnetic field and the normal to the plane of the loop is ? rads and is decreasing at the rate of 0.50 rad/s, what is the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop?
a. zero
b. 13 mV
c. 26 mV
d. 20 mV
a
You might also like to view...
If the polar ice decreases, what would happen, and why?
A) cooling, because melted ice cools things off B) warming, because more sunlight is reflected C) cooling, because more sunlight is reflected D) warming, because more sunlight is absorbed
A thin copper rod 1.00 m long has a mass of 50.0 g. What is the minimum current in the rod that would allow it to levitate above the ground in a magnetic field of magnitude 0.100 T?
1.1.20 A 2.2.40 A 3.4.90 A 4.9.80 A 5.none of those answers
The wedge-shaped cavity shown in the accompanying sketch consists of two long strips joined along one edge. Surface 1 is 1-m-wide, has an emittance of 0.4, and has a temperature of 1000 K. The other wall has a temperature of 600 K. Assuming gray diffuse processes and uniform flux distribution, calculate the rate of energy loss from surface 1 and 2 per meter length.
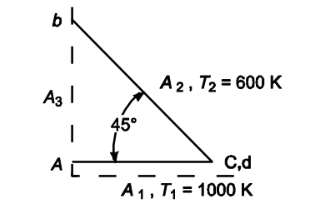
GIVEN
• The wedge shaped cavity shown above
• Width of A1 (W1) = 1 m
• Emittance of A1 (?1) = 0.4
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 1000 K
• Temperature of A2 (T2) = 600 K
• A2 is black
FIND
• The rate of energy loss from A1 and A2 per meter length (q1/L and q2/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Enclosure temperature (Te) = 0 K
• Gray diffuse processes
• Uniform flux distribution
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
If a 5.0 kg box is pulled simultaneously by a 10.0 N force and a 5.0 N force, then its acceleration must be
A) 3.0 m/s2. B) 2.2 m/s2. C) 1.0 m/s2. D) We cannot tell from the information given.