Suppose that, at the market clearing price of natural gas, the price elasticity of demand is -1.2 and the price elasticity of supply is 0.6. What will result from a price ceiling that is 10 percent below the market clearing price?
A More information is needed.
B A shortage equal to 1.8 percent of the market clearing quantity
C A shortage equal to 0.6 percent of the market clearing quantity
D A shortage equal to 18 percent of the market clearing quantity
E A shortage equal to 6 percent of the market clearing quantity
D A shortage equal to 18 percent of the market clearing quantity
You might also like to view...
The aggregate supply curve shifts
A) rightward if potential GDP decreases. B) rightward if the money wage rate falls. C) leftward if the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward. D) rightward if the money wage rate rises. E) leftward if potential GDP increases.
The LM curve represents combinations of income and interest rate which
A) clear the goods market. B) achieve the external equilibrium. C) clear the money market. D) achieve internal equilibrium.
The aggregate M1 consists of
A) currency plus all deposits in financial institutions. B) currency plus all deposits in all institutions. C) currency plus checkable deposits in financial institutions. D) currency plus all checkable deposits.
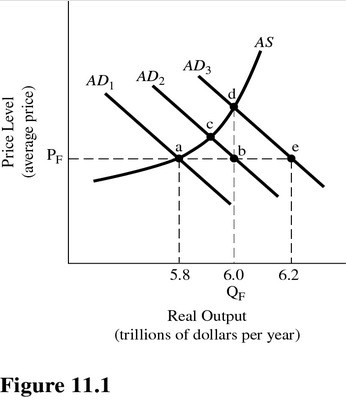 Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion. The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
A. $.2 trillion. B. $.6 trillion. C. $.4 trillion. D. None of the choices are correct.