In the long run in monopolistic competition, firms
A) can earn an economic profit.
B) incur an economic loss.
C) can earn zero economic profit but not an economic profit.
D) shut down if they are earning zero economic profit.
E) earn either an economic profit or zero economic profit.
C
You might also like to view...
The sustainable upper limit of real GDP is a level of GDP that is
A) greater than potential GDP, but by how much greater is unknown and controversial. B) less than potential GDP, but by how much less is unknown and controversial. C) potential GDP. D) determined only by what is the full employment equilibrium in the labor market. E) None of the above answers is correct because there is no sustainable upper limit to real GDP because real GDP can always be increased.
In the ____________, households work and receive payment from firms.
A. financial investment market B. financial capital market C. labor market D. savings market
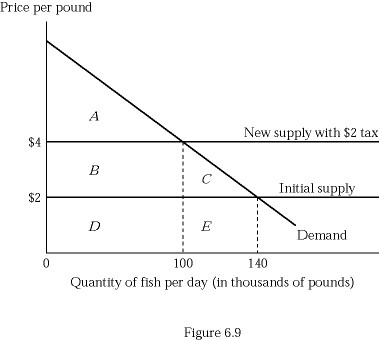 Figure 6.9 depicts a hypothetical fish market with a horizontal supply curve. The consumer surplus at the new equilibrium with $2 tax is shown by:
Figure 6.9 depicts a hypothetical fish market with a horizontal supply curve. The consumer surplus at the new equilibrium with $2 tax is shown by:
A. Triangle A. B. Triangle A + Rectangle B. C. Rectangle B + Triangle C. D. Triangle C + Rectangle E.
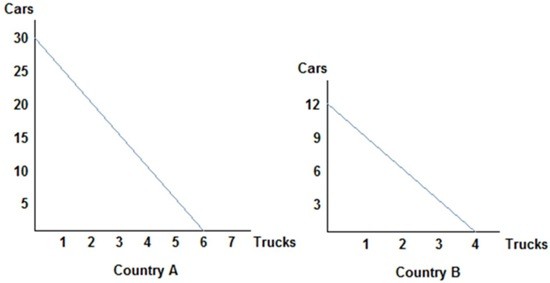 Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. After comparing each country's production possibilities curve, it is clear that:
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. After comparing each country's production possibilities curve, it is clear that:
A. Country B will lose by trading with Country A. B. Country A should specialize in trucks and Country B should specialize in cars, and both will benefit from trade. C. Country A should specialize in cars and Country B should specialize in trucks, and both could benefit from trade. D. Country A will not benefit from trade.