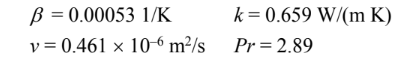How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 2.00 moles of an ideal monatomic gas by 10°C at constant volume? (R = 8.31 J/mol ? K)
A) 249 J
B) 416 J
C) 208 J
D) 200 J
E) 125 J
A
You might also like to view...
To measure thermal conductivity, two similar 1-cm-thick specimens are placed in an apparatus shown in the accompanying sketch. Electric current is supplied to the 6-cm by 6-cm guarded heater, and a wattmeter shows that the power dissipation is 10 watts (W). Thermocouples attached to the warmer and to the cooler surfaces show temperatures of 322 and 300 K, respectively. Calculate the thermal conductivity of the material at the mean temperature in W/(m K).
GIVEN
Thermal conductivity measurement apparatus with two samples as shown
Sample thickness (L) = 1 cm = 0.01 cm
Area = 6 cm ? 6 cm = 36 cm2 = 0.0036 m2
Power dissipation rate of the heater (qh) = 10 W
Surface temperatures
Thot = 322 K
Tcold = 300 K
FIND
The thermal conductivity of the sample at the mean temperature in W/(m K)
ASSUMPTIONS
One dimensional, steady state conduction
No heat loss from the edges of the apparatus
SKETCH
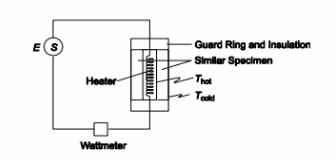
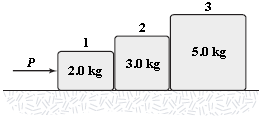
If P = 6.0 N, what is the magnitude of the force exerted on block 1 by block 2?
a.
6.4 N
b.
5.6 N
c.
4.8 N
d.
7.2 N
e.
8.4 N
Bones show up in x ray images because they absorb x rays more efficiently than muscle and other tissues do
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Compare the rate of condensate flow from the pipe in Problem 8.28 (air pressure = 200 kPa) with that for a 3.89-cm-OD pipe and 200 kPa air pressure. What is the rate of condensate flow if the 2 cm pipe is submerged in a 20°C constant-temperature water bath?
GIVEN
• A long horizontal copper pipe carrying saturated steam within an environmental testing chamber or a water bath
• Steam pressure = 120 kPa
• Ambient pressure (P) = 2 atm
• Ambient air or water temperature (T?) = 20°C
FIND
Rate of condensate flow for
(a) Diameter (D) = 3.89 cm = 0.0389 m Fluid is air at 2.0 atm
(b) Diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m Fluid is water at T? = 20°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Pressure change has no effect on absolute viscosity, thermal conductivity, or specific heat of the air
• Air is still
• Convective thermal resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the copper pipe is negligible
• The air behaves as an ideal gas
SKETCH
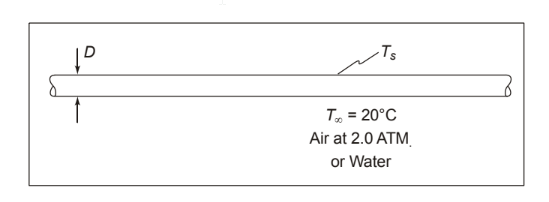
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For saturated steam at 0.12 MPa, the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2238 kJ/kg, and the temperature (Ts) = 105°C.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 62.5°C and one atmosphere
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00298 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0281 W/(m K)
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 at P = 2.0 Atm,
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 9.83 × 10–6 Ns/m2