Consider two labor markets in which jobs are equally attractive in all respects other than the wage rate. All workers are equally able to do either job. Initially, both labor markets are perfectly competitive. If a union organizes workers in one of the markets, then wage rate will tend to
a. rise in both markets
b. fall in both markets
c. rise for the union job, but remain unchanged for the nonunion job
d. fall for the nonunion job, but remain unchanged for the union job
e. rise for the union job and fall for the nonunion job
E
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is NOT a result of a temporary fall in foreign demand on one country's exports under floating exchange rate?
A) The DD curve shifts to the left due to reduction of aggregate demand. B) The AA curve shifts downwards due to reduction of money supply. C) a fall in aggregate output D) depreciation in home country's currency E) a fall in the home interest rate
Vince says that the present value of $500 to be received one year from today if the interest rate is 8 percent is more than the present value of $500 to be received two years from today if the interest rate is 4 percent. Terri says that $500 saved for two years at an interest rate of 3 percent has a larger future value than $500 saved for one years at an interest rate of 6 percent
a. Both Vince and Terri are correct. b. Only Vince is correct. c. Only Terri is correct. d. Neither Vince nor Terri is correct.
Below, the graph on the left shows the short-run cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive market, and the graph on the right shows the current market conditions in this industry. In order to maximize profit, how much output should the firm produce?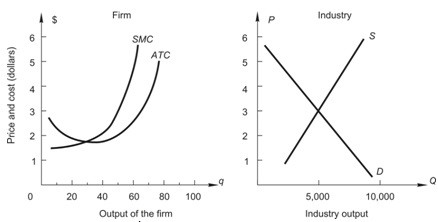
A. 60 units B. 80 units C. 20 units D. 40 units E. 50 units
A year-long drought that destroys most of the summer's crops would be considered a:
A. short-run supply shock. B. long-run demand shock. C. long-run supply shock. D. short-run demand shock.