Suppose the Swiss franc rises against the British pound but falls against the Japanese yen. What happens to the prices of goods imported into Switzerland?
A) Both British and Japanese goods fall in price.
B) Both British and Japanese goods rise in price.
C) British goods rise in price while Japanese goods fall in price.
D) British goods fall in price while Japanese goods rise in price.
D
You might also like to view...
The amount of work a person will do as wage increases depends entirely on the size of the wealth effect. ?
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Figure 5-16
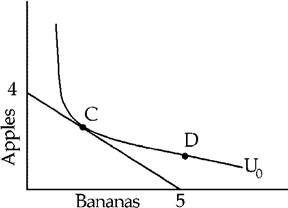
In Figure 5-16, Adam is
a.
better off at C than at D and able to afford either C or D.
b.
better off at D than at C but only able to afford C.
c.
equally well off at C and D and able to afford either C or D.
d.
equally well off at C and D but only able to afford C.
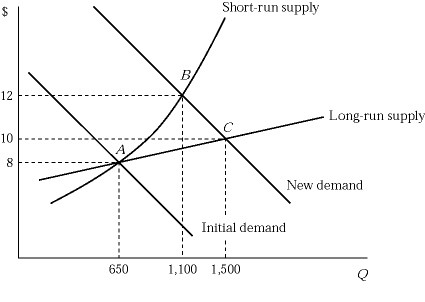 Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. If the market demand curve shifts to the right, which of the following statements is true in the long run?
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. If the market demand curve shifts to the right, which of the following statements is true in the long run?
A. The market price drops below $12 as more firms enter the market and build more plants. B. Both existing firms and new firms earn a zero economic profit. C. All firms in the industry maximize their profits by producing the output where the marginal cost equals $10. D. All of these are correct.
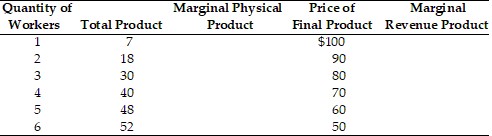 In the above table, if the marginal factor cost is $480, how many workers would be hired?
In the above table, if the marginal factor cost is $480, how many workers would be hired?
A. 6 B. 5 C. 3 D. 4