When does a star become a main-sequence star?
A) when the protostar assembles from a molecular cloud
B) the instant when hydrogen fusion first begins in the star's core
C) when the rate of hydrogen fusion within the star's core is high enough to maintain gravitational equilibrium
D) when a star becomes luminous enough to emit thermal radiation
E) when hydrogen fusion is occurring throughout a star's interior
C
You might also like to view...
What circumstances produce stationary patterns in interfering waves?
a. The waves have to be stationary (i.e., not move). b. The waves have to have the same amplitude. c. The waves need to have the same wavelength but different frequencies. d. The waves have to have the same wavelength and a constant phase difference. e. The waves have to have the same wavelength and varying phase differences.
Conductors: A thin spherical copper shell of radius 9.5 cm carries an excess charge of -4.2 nC. How many excess electrons are on (a) the outer surface of the shell, and (b) the inner surface? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C)
What will be an ideal response?
A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s from the edge of a building of a certain height. The ball lands at a horizontal distance of 82.0 m from the base of the building. What is the height of the building?
A) 40.5 m B) 60.2 m C) 87.9 m D) 82.4 m E) 50.4 m
Quantum issues often constrain transitions in quantum harmonic oscillators to those where ?n = 1. Consider a spectrum chart (like the one shown in figure Q11.2) for such a system. What would this chart look like?
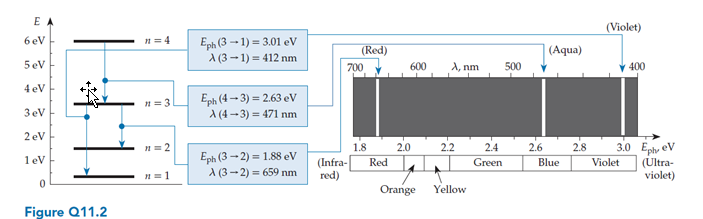
A. There would be only one emission line.
B. The emission lines would be evenly spaced in energy.
C. The emission lines would become more closely spaced (in energy) as we go to the right.
D. The emission lines would become farther apart (in energy) as we go to the right.