The fulfillment function of the business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce cycle is responsible for delivering products or services to customers
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
True
You might also like to view...
Brands that seek to remove or restrict material from the Internet are often sanctioned in a very public and humiliating manner. Also known as the Streisand effect, it is important to consider the ramifications of online content because ________.
A. the content might be ineffective. B. more research is needed. C. it could be the wrong platform for the information. D. there could be errors in the content. E. whatever content goes online tends to stay online forever
Copyrights in Digital Information. Sega Enterprises, Ltd., develops and markets video entertainment systems, including the "Genesis" console and video game cartridges. Accolade, Inc, is an independent developer, manufacturer, and marketer of computer
entertainment soft-ware, including game cartridges that are compatible with Genesis and other computer systems. Sega licenses its copyrighted computer code and its trademark to developers of Genesis-compatible games in competition with Sega. Accolade chose not to purchase a license from Sega, however, but to reverse engineer Sega's games to discover the requirements of the code that would make Accolade's games compatible with Genesis. As part of the reverse engineer-ing, Accolade transformed the machine-readable object code contained in Sega's game car-tridges into human-readable source code using a process called "disassembly." At the end of the process, Accolade created a manual that incorporated the information it had discovered about the requirements for a Genesis-compatible game. The manual did not include any of Sega's code. With the manual, Accolade created a new computer code; with this code, Acco-lade developed Genesis-compatible games. Sega sued Accolade, claiming, among other things, that Accolade's disassembly of its computer program constituted copyright infringement. Accolade contended that its disassembly of the code was a fair use. How should the court rule? Discuss fully.
Which of the following special cases does not require reformulation of the problem in order to obtain a solution?
a. alternate optimality b. infeasibility c. unboundedness d. each case requires a reformulation.
The firm's before-tax cost of debt is ________.
A firm has determined its optimal capital structure which is composed of the following sources and target market value proportions.
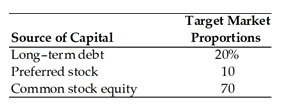
Debt: The firm can sell a 12-year, $1,000 par value, 7 percent bond for $960. A flotation cost of
2 percent of the face value would be required in addition to the discount of $40.
Preferred Stock: The firm has determined it can issue preferred stock at $75 per share par value. The stock will pay a $10 annual dividend. The cost of issuing and selling the stock is $3 per share.
Common Stock: A firm's common stock is currently selling for $18 per share. The dividend expected to be paid at the end of the coming year is $1.74. Its dividend payments have been growing at a constant rate for the last four years. Four years ago, the dividend was $1.50. It is expected that to sell, a new common stock issue must be underpriced $1 per share in floatation costs. Additionally, the firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent.
A) 7.8 percent
B) 10.6 percent
C) 11.2 percent
D) 12.7 percent